Are RV Breakers the Same as Home Breakers? Essential Comparisons
RV breakers and home breakers are similar in function but differ in ampere ratings and layout; understanding these variances is crucial for safe electrical use in RVs.
Circuit breakers are crucial for the safety of both RVs and homes. They stop the flow of electricity when there is too much current, preventing damage like fires. Although they have similar functions, there are seven key differences between RV and home breakers.
This post will explain these differences, ensuring the safe and efficient use of electricity in both settings.
Disclosure: As an Amazon Associate, this site earns from qualifying purchases. Thank you!
How Does the Electrical System Work in an RV?
In an RV, the electrical system is divided into two main categories: Direct Current (DC) and Alternating Current (AC). The 12 Volt DC system controls the exterior lighting related to driving or towing your camper, like headlights, marker lights, brake lights, and signal lights.
This originates from the tow vehicle’s battery for trailers, or the chassis on class A or C units. It is charged by the alternator while the engine is running.
The DC system also extends to the interior of the RV, powering devices such as the water pump, refrigerator, furnace fan, and other appliances that run on 12 volts. The power for this system comes from the RV’s battery, which can be charged either by the vehicle’s electrical system or by an AC charger when connected to a power outlet.
On the other hand, the AC electrical system in an RV is similar to the one found in your home. It powers high-voltage appliances such as air conditioners, microwave ovens, and electric heaters. This system is usually sourced from an external power supply at a campsite or generated by an onboard generator.
Circuit breakers and fuses are integral components of both the DC and AC electrical systems in an RV. They control and protect the flow of electricity throughout the vehicle. When too much electricity flows through the system, possibly due to an overload or short circuit, the circuit breaker will trip, stopping the flow and preventing any potential damage.
Fuses serve a similar purpose in the DC system. When a fuse experiences an overload, it will blow, breaking the circuit and stopping the flow of electricity. In both cases, once the issue causing the overload is resolved, the breaker can be reset or the fuse replaced, and the circuit can be safely re-energized.
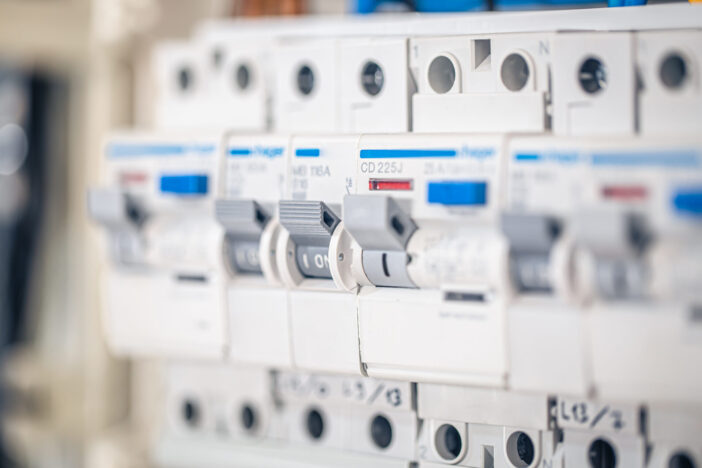
Are RV Breakers the Same as Home Breakers?
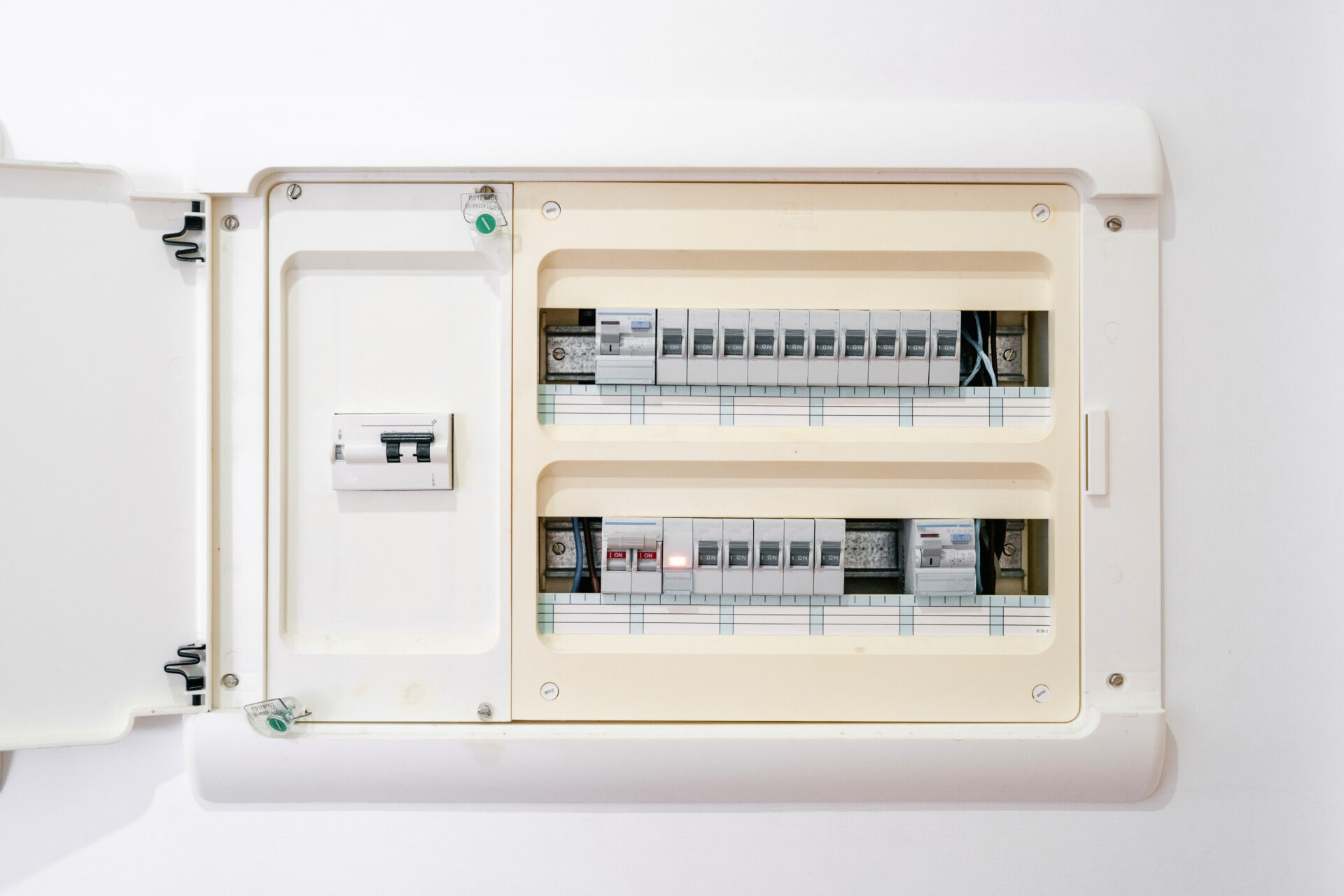
At a fundamental level, RV breakers and home breakers perform the same function: they protect electrical circuits from overloads or short circuits by halting the flow of electricity when the current exceeds a certain limit.
Both types of breakers are designed to be reset once they have tripped, unlike fuses which need to be replaced when they blow.
Moreover, the three main types of circuit breakers found in homes – standard, GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter), and AFCI (Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter) – can also be found in RVs. These different types of breakers offer varying levels of protection suitable for different applications within the electrical system.
Despite these similarities, RV breakers and home breakers are not exactly the same. One of the key differences lies in their ampere ratings.
Because RVs typically have fewer and smaller appliances compared to a home, the circuit breakers in an RV usually have lower ampere ratings. For instance, while a typical home breaker might be rated for 15 or 20 amps, an RV breaker might only be rated for 10 or 15 amps.
Another difference is that some breakers in an RV can serve more than one circuit, with each side of a dual breaker potentially having a different value. This is less common in the typical home where both sides of a dual breaker are usually of the same value.
The layout and construction of RV breaker boxes also differ from those found in homes. For instance, due to space constraints, RV breaker boxes tend to be more compact. In addition, they are often designed to withstand the vibrations and movements experienced while driving.
Understanding Your RV Electrical Panel
Understanding your RV’s electrical panel is crucial to the safe and efficient operation of all electrical devices on board. Knowing how the panel works allows you to control the flow of electricity throughout your RV, enabling you to switch off certain circuits when not in use or when performing maintenance tasks.
It can also help you identify overloaded circuits that may cause the breakers to trip frequently. Aside from ensuring efficient use of electricity, a good grasp of your RV’s electrical system can prevent potential damage. Overloading a circuit can lead to overheating, damaging not just the wiring but also the connected devices.
Moreover, it can increase the risk of electrical fires. Being able to properly manage your RV’s electrical load, therefore, contributes significantly to the safety and longevity of your RV.
Furthermore, understanding your RV’s electrical panel allows you to troubleshoot issues more effectively. For example, if a certain device isn’t working, you can check if its corresponding circuit breaker has tripped or if the fuse has blown.
If your breakers are frequently tripping, this could indicate an underlying issue with your RV’s electrical system that needs to be addressed.
Understanding the differences between RV breakers and home breakers, as well as the function and importance of your RV’s electrical system, is key to the safe and efficient use of electricity in your RV. Whether you’re a seasoned RVer or a beginner, being knowledgeable about these aspects will undoubtedly enhance your RVing experience.






